Reduction Can Convert an Aldehyde Into a Secondary Alcohol.
126 Ch 7 Alcohols Thiols Phenols Ethers. Alcohol dehydrogenases ADH EC 1111 are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD to NADHIn humans and many other animals they serve to break down alcohols that otherwise are toxic and they also.

19 6 Oxidation Of Alcohols Aldehydes Organic Chemistry Ii
Carbonyl synthesis by-product of butanol production from propylene.
. Also reoxidized the alcohol with DMP back to the aldehyde in 63 or 87 total from ester - aldehdye That reduction was following a Frater-Seebach alkylation which was a pain to run -40. This route can be advantageous compared to traditional borylation reactions by making use of cheap and abundant hydrocarbon starting material limiting prefunctionalized organic compounds reducing toxic byproducts and streamlining the synthesis of biologically. Metal-catalyzed CH borylation reactions utilize transition metals to directly convert a CH bond into a CB bond.
However direct electrochemical reduction of CO 2 can have a number of advantages compared to hydrogenation of CO 2 or CO by electrochemically produced H 2. As shown above mild reagents stop the oxidation once the. When an aldehyde is introduced to the Tollens reagent two things occur.
In pure alcohol systems extra. The Cr is reduced VI IV the alcohol is oxidized. Depending on the nutritional hormonal energetic status the acetyl CoA is converted to the indicated products.
This reagent is being replaced in laboratories by DessMartin periodinane DMP which has several practical advantages over PCC such as producing. Alcohol is oxidized by alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenases eventually to acetyl CoA. Oxidation of Primary Alcohols Primary alcohols are easily oxidized just like secondary alcohols and.
The carbon the alcohol is secondary and three alkyl groups attached the alcohol is tertiary. The reading mentions that pyridinium chlorochromate PCC is a milder version of chromic acid that is suitable for converting a primary alcohol into an aldehyde without oxidizing it all the way to a carboxylic acid. In contrast FeTiO 2 activates the alcohol mildly without forming aldehyde and hydrogen atoms under irradiation allowing a direct dehydrative coupling of the activated alcohol with aniline to.
RCH 2OH RCHOH R RCOH R R primary secondary tertiary 71b Physical Properties of Alcohols Many of the physical properties of alcohols are directly related to the hydrogen bonding exhibited by the hydroxyl group. This reaction can be written as follows. The use of PhIOAc 2 in dichloromethane enables a clean oxidative cleavage of 12-diols to aldehydes.
Secondary organic aerosols SOA are crucial constitution of fine particulate matter PM which are mainly derived from photochemical oxidation products of primary organic matter and volatile organic compounds VOCs and can induce terrible impacts to human health air quality and climate change. Secondary alcohols can only be oxidized to ketones while primary alcohols are oxidized to aldehydes and carboxylic acids depending on whether a mild or strong oxidizing agent is used. The silver ions present in the Tollens reagent are reduced into metallic silver.
Using propylene and synthesis gas as raw material going through carbonyl synthesis in the system to get n-butyl and isobutyl aldehyde after the catalyst hydrogenating into alcohol then undergoing dehydration and separation can obtain the product of n-butyl and isobutyl alcohol respectively. Alcohols can be oxidized into a variety of carbonyl compounds depending on the nature of the alcohol and the oxidizing agent used. Lett 2004 6 217-219.
Step 1 catalyzed by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase which is present largely in the liver and consists of a family of isoforms. Interchanging any three groups on a carbon does a bond. The alcohol and chromic acid produce a chromate ester which then reductively eliminates the Cr species.
The RhTiO 2 promotes the photocatalytic dehydrogenation of alcohol into aldehyde and molecular hydrogen resulting in rapid condensation of aldehyde with aniline to yield imine. As we know organosulfates OSs and organic nitrates ON are important. A vitamin-related cofactor nicotinamide adenine.
This sets us up to form a bond between the C 5-OH and the carbonyl carbon C-1 which will make a new ringIf this is unclear see this earlier post on ring-chain tautomerism for more examplesIts helpful to perform a bond rotation on the C 5 carbon to make the stereochemistry on the ring clearer. Secondary alcohols can be chemoselectively converted into ketones in the presence of primary hydroxy groups. It 1 combines the electrochemical water splitting and subsequent thermal hydrogenation into a single electrochemical process 2 enables products that cannot easily be prepared by thermally.
The aldehyde is oxidized by the Tollens reagent and forms a carboxylic acid. 68 yield of aldehyde 30 yield of alcohol. Generally the Tollens Test is carried out in clean test tubes made of glass.

Ch15 Reduction Of Aldehydes And Ketones
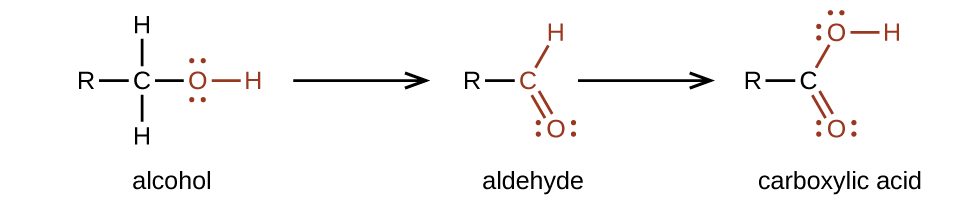
20 3 Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic Acids And Esters Chemistry

Oxidation Of Alcohols By Potassium Permanganate The Mechanism Chemistry Education Chemistry Basics Organic Chemistry

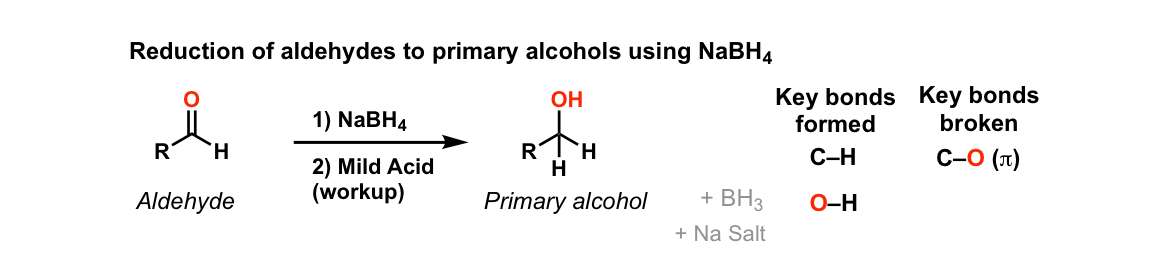
Addition Of Nabh4 To Aldehydes To Give Primary Alcohols Master Organic Chemistry
No comments for "Reduction Can Convert an Aldehyde Into a Secondary Alcohol."
Post a Comment